Molluscum Contagiosum: Symptoms Of Molluscum Contagiosum
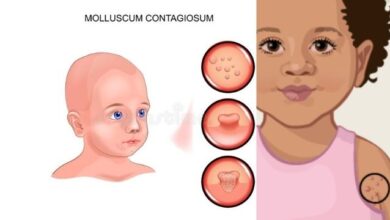
A virus called Molluscum Contagiosum causes a skin condition with the same name. On the upper layers of your skin, it causes moderate, raised lumps, or ulcers.
In most cases, the little pimples are painless. They go away on their own and rarely leave scars. The duration of the infection varies from person to person, but the pimples can continue anywhere from two months to four years.
Molluscum Contagiosum (M. Contagiosum) is spread between people through direct skin contact with a virus-infected person or by touching a contaminated object, such as a towel or a piece of clothing.
Treatments such as medication and surgery are available, but you won’t need them almost all of the time. If you have a compromised immune system, the virus will be much more difficult to cure or have more severe consequences.
The symptoms, causes, and treatments for molluscum Contagiosum are discussed in this article.
Symptoms Of Molluscum Contagiosum
You or your child may not show symptoms of infection for up to 6 months after getting in contact with the M. Contagiosum virus. From the time you contract the Molluscum Contagiosum virus, these symptoms usually appear in 2 to 7 weeks.
A tiny collection of painless blisters may appear on your skin. These lumps can develop singly or in groups of up to 20.
Typically, they’re:
- It has a very tiny, gleaming, and smooth form.
- Pink, white, or flesh-colored
- Solid and dome-shaped, with a depression or dimple at the center.
- Packed with a waxy substance center core.
- Present on the face, belly, chest, arms, and legs of youngsters, and the inner thigh, genitals, and abdomen of adults, but not on the palms of your hands or the soles of your feet.
Complications Of Molluscum Contagiosum
The majority of molluscum Contagiosum cases heal on their own. However, certain persons have difficulties, such as:
- Impetigo is a skin infection that occurs when sores are scratched.
- Conjunctivitis is an infection of the eyelid that can develop if lesions appear on it.
- Secondary eczema, which might develop as a result of your immune system’s hypersensitivity to the infection.
- widespread molluscum Contagiosum that are larger than usual, often on the face.
- Scarring with a pitted look that occurs suddenly, either naturally or as a result of lesion removal surgery.
Causes Of Molluscum Contagiosum
Whenever you obtain the M. Contagiosum virus, a type of poxvirus, you have Molluscum Contagiosum.
While scars are observable, this virus can spread between people. It’s also possible to spread the virus from one area of your body’s skin to another.
Molluscum Contagiosum Transmission
M. Contagiosum can spread between people in a variety of ways, including:
- Contact with a person who has the infection on their skin
Molluscum Contagiosum is contracted by contacting the sores on the skin of someone who has the infection. Viruses can be passed from child to child during typical play.
Sexual interaction is more likely to infect teenagers and adults. Infection can also occur during contact sports involving naked skin contact, such as wrestling or football.
- Contact with surfaces that have been touched by someone who has Molluscum Contagiosum
On surfaces that have come into contact with the skin, the virus can survive. By handling contaminated towels, clothing, toys, or other items, you can get the virus.
- Sharing sporting equipment that has come into contact with someone who has Molluscum Contagiosum is not a good idea
The virus can survive on equipment and be passed on to someone else. Baseball gloves, wrestling mats, and football helmets are examples of this.
- Internal spread
You could spread Molluscum Contagiosum throughout your body if you have it. By rubbing, scratching, or shaving a lump and then contacting another part of your body, you can spread the virus from one region of your body to another.
Transmission appears to be more prevalent in wet conditions, such as during communal swimming lessons for children. The virus can no longer transfer from your body to another’s if skin sores are no longer visible.
Read Also:
What is Cervical Cancer: Cancer Test Wait Putting, A Report
Molluscum Contagiosum Risk Factors
Molluscum Contagiosum can affect everyone, although certain groups of people are more likely to contract the virus and develop symptoms than others. The following are some of these organizations:
- Between the ages of one and ten years.
- Those who live in tropical environments.
- People who have had their immune systems reduced by organ transplants, cancer treatments, or illnesses that damage the immune system, such as HIV.
- Those who suffer from atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema that creates scaly, itchy rashes.
- Wrestlers and football players are examples of persons who participate in contact sports where skin-to-skin contact is widespread.
Molluscum Contagiosum Diagnosis
Molluscum Contagiosum causes skin lumps that have a characteristic look. As a result, your doctor may be able to identify Molluscum Contagiosum just by looking at the affected area.
A skin scraping or biopsy may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
So although Molluscum Contagiosum is unlikely to accept treatment, you should always have any skin lesions that stay more than a few days examined by your doctor.
A verified diagnosis of Molluscum Contagiosum eliminates the possibility of alternative causes, such as:
- Skin Cancer
- Chickenpox
- warts
Molluscum Contagiosum Treatment
Molluscum Contagiosum does not require therapy for most persons with a good immune system. These pimples normally go away on their own without the need for medical attention.
When To See A Doctor About Molluscum Contagiosum
You may be a good candidate for treatment if you have the following circumstances:
- You have a health concern that produces skin consequences, such as atopic dermatitis.
- Your lesions are huge and centered on your face and neck.
- You’re worried about spreading the virus.
- You’ve had treatment, or you’ve developed a health problem that lowers your immune activity.
Medical Treatments For Molluscum Contagiosum
A doctor can treat Molluscum Contagiosum with one of numerous successful treatments. These are some of them:
- Cryotherapy– The doctor uses liquid nitrogen to freeze each bump.
- Curettage– The doctor uses a small tool to penetrate the lump and scrape it off the skin.
- Laser therapy– is a type of treatment that involves the use of The doctor destroys each bump with a laser.
- Topical therapy– is a type of treatment that is applied to the skin To stimulate peeling of the top layers of the skin, the doctor administers lotions containing acids or chemicals to the pimples. Iodine and salicylic acid, tretinoin, cantharidin (a blistering agent used by a doctor), and imiquimod are all common ingredients in topical therapy creams (T cell modifier).
For some people, these treatments might be painful and leave scars. During the procedure, anesthesia may be required.
Because these approaches involve treating each bump individually, a process may necessitate multiple sessions. If you have a lot of huge bumps, you may need extra treatment every 3 to 6 weeks until they go away. As the present bumps heal, more ones may appear.
Prescribed Medications For Molluscum Contagiosum
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Iodine and salicylic acid creams or potassium hydroxide trichloroacetic acid creams
- Podophyllotoxin cream is a topical treatment for podophyllotoxin poisoning (Condylox).
- Cantharidin (Cantharone), a blistering substance commonly applied by a doctor.
- T cell modulator imiquimod (Aldara) (however the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do not suggest its use in children because it has not been proven beneficial and can produce serious side effects).
If you’re pregnant, expecting to get pregnant, or breastfeeding or chestfeeding, inform your doctor before using these or any other medications.
When persons with HIV get Molluscum Contagiosum, antiretroviral medication (ART) is the most effective treatment. It can aid in the strengthening of the immune system and the battle against the infection.
Molluscum Contagiosum Preventions
The easiest strategy to avoid contracting Molluscum Contagiosum is to avoid touching the infected skin of another person. Following these tips can also help you prevent the infection from spreading:
- Hands should be washed thoroughly with warm water and soap.
- Children are more likely to utilize contact in play and connection with others, so teach them how to wash their hands properly.
- Personal items should not be shared. Towels, apparel, hairbrushes, and bar soaps are all examples.
- Avoid sharing sporting equipment that has come into direct contact with another person’s exposed skin.
- Picking or touching the visible bumps on your skin is not a good idea.
- To avoid yourself or others from touching the bumps and spreading the virus, keep them clean and covered.
- Where the bumps are located, avoid shaving or electrolysis.
- If you have bumps in your genital area, avoid sexual contact.
Conclusion
Molluscum Contagiosum is not a dangerous condition in general. In most cases, it will go away on its own within 6 to 12 months. However, like with any disease, precautions should be taken to prevent it from spreading. Also, if your symptoms seem to be becoming worse, you should see a doctor.
Disclaimer
The information on this site is provided solely for educational reasons and is not intended to replace medical treatment provided by a healthcare professional. Because each person’s needs are different, the reader should check with their doctor to see if the material is appropriate for them.
FAQ
Q- Is molluscum Contagiosum a sexually transmitted disease?
A- Molluscum Contagiosum is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can be communicated during intercourse through skin-to-skin contact. Small, smooth, spherical, pearly lumps with a central core characterize it. Although the infection normally disappears on its own, therapy can help to minimize the duration of symptoms.
Q- How can you get rid of Molluscum Contagiosum the quickest?
A- Cryotherapy involves applying an extremely cold material to each molluscum lump by your dermatologist. The bumps can be successfully destroyed by the intense cold. Because new molluscum can form, you’ll need to come back every 2 to 3 weeks for treatment until the bumps disappear.
Q- Why Adults obtain molluscum?
A- Molluscum Contagiosum can affect both teens and adults. It is usually contracted during sexual intercourse. Molluscum is considered a sexually transmitted infection when this happens (STI). When molluscum is contracted through sexual contact, pimples appear on (and around) the genitals.
Q- Is it necessary to pop molluscum bumps?
A- They continue to increase in size and form white or yellow pus-filled caps, often with a distinctive depression, as time passes (third image from the left – the purulent stage). These can be popped, however it is not recommended because it can spread the infection.
Q- When it comes to molluscum, how long does it last?
A- Molluscum Contagiosum usually heals without scars in 6-12 months, however it might take up to 4 years.



